
views
X
Research source
Understanding Patents as an Intangible Asset

Define patents as a type of intangible asset. Similar to a copyright, trademark, trade name, franchise license, government license, etc., patents are considered to be "intangible." A company only has the rights to a patent for a limited amount of time. Examples of tangible assets are land, buildings, vehicles and equipment.
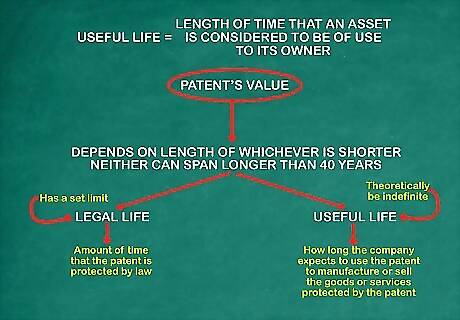
Define useful life. This is the length of time that an asset is considered to be of use to its owner. For example, when a pharmaceutical company receives a patent on a new drug, it is only for a specific period of time, such as 20 years. After that time other pharmaceutical companies can produce the same type of drug. Therefore its useful life is 20 years. If you needed to estimate the useful life of a trademark such as kleenex, for example, you could look up information on the Internet for estimates of useful lives of similar trademarks. The patent's value is dependent on the length of either its useful life or its legal life, whichever is shorter, but neither can span longer than 40 years. The patent's legal life is the amount of time that the patent is protected by law, while its useful life is how long the company expects to use the patent to manufacture or sell the goods or services protected by the patent. The useful life might theoretically be indefinite, while the legal life of the patent has a set limit. On the other hand, the company may find that their expected useful life is shorter than the legal life, especially in a rapidly evolving industry. In either case, the shorter of the two lives is used.
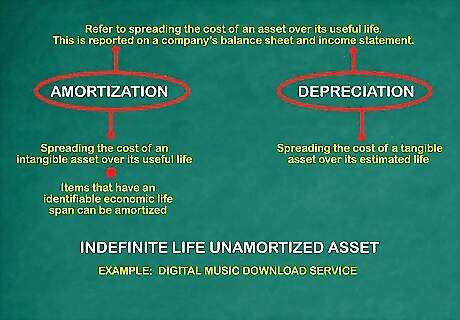
Define amortization vs. depreciation. Both amortization and depreciation refer to spreading the cost of an asset over its useful life. This yearly amount is reported on a company's balance sheet and income statement. Amortization refers to spreading the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. Depreciation refers to spreading the cost of a tangible asset over its estimated life. Since patents are intangible, they are amortized. Only items that have an identifiable economic life span can be amortized. Other intangible assets that have an indefinite life span are not amortized, but instead are evaluated for relevancy or destruction from time to time. If these assets never show a decrease in relevance or destruction of any sort, the indefinite life assets will remain on your balance sheet permanently. An example of an indefinite life, unamortized asset would be a digital music download service. As long as the service is free from destruction and continues to be economically relevant, it remains on a balance sheet.
Calculating Amortization on Patents
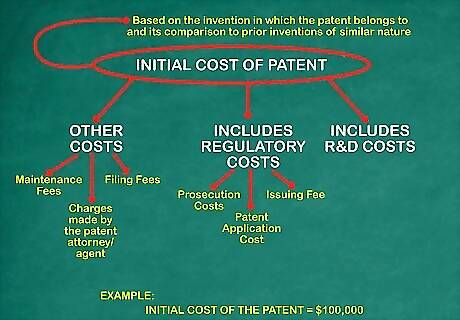
Determine the initial cost of the patent itself. A patent's initial cost is based on the invention in which the patent belongs to and its comparison to prior inventions of similar nature. For this example, the initial cost of the patent will be $100,000. You could also add up all the research and development costs incurred to design the invention. R&D costs are expensed until future economic benefits are probable, then future costs (called engineering and development costs) are capitalized (added to the intangible asset - patent account) and amortized. Patent costs go far beyond the initial cost of development. Some of the regulatory costs include patent application cost, prosecution costs to verify is originality, and an issuing fee. Maintenance fees also are charged every 3.5, 7.5, and 11.5 years to continue the patent's validity. There is also a filing fee which is dependent on the number of claims associated with the invention's particular application, which typically ranges from $400 to $1000 or more. The highest charges for most patent applicants are the charges made by the patent attorney or agent that prepares the actual patent application.
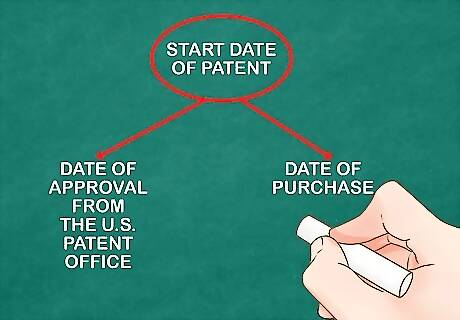
Determine the start date of the patent. Amortization of patents begins when it is acquired or when it is available for use. For example, this would be the date a patent was purchased or when approval was received from the U.S. Patent Office.
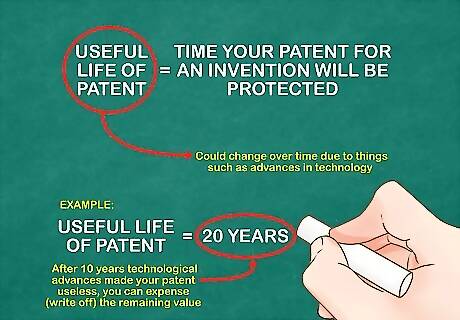
Obtain the length of the patent's estimated useful life. You will need to find out the duration of the patent. For example, imagine that your patent for an invention will be protected for 10 years, as stated when the patent was first granted. This will be the useful life of your patent. However, the useful life of a patent could change over time due to things such as advances in technology. For example, if you assumed the patent was useful for 20 years, but after 10 years technological advances made your patent useless, you can expense (write off) the remaining value.
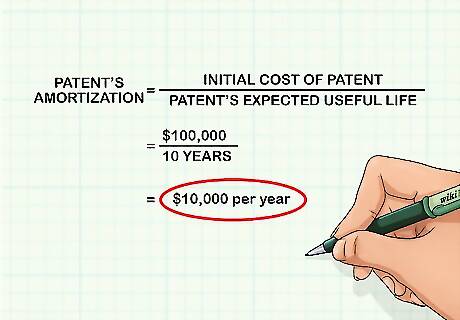
Calculate the patent's amortization. Divide the value of the initial cost of the patent by the patent's expected useful life. The result is the amortization of the patent. For this example, the initial cost is $100,000 and the useful life span is 10 years; therefore, the patent's amortization is $100,000 / 10 years = the patent's amortization amount of $10,000 per year.
Recording Amortization on Financial Statements
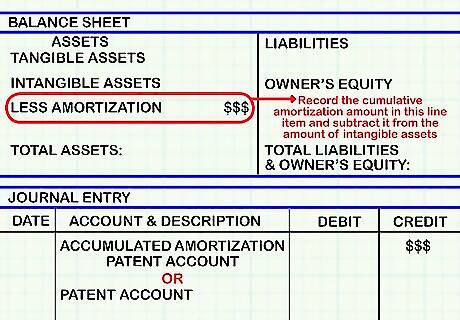
Record the amount of amortization on the company's balance sheet. A line item will exist on the balance sheet for intangible assets. A line under this will say "Less Amortization." Record the cumulative amortization amount in this line item and subtract it from the amount of intangible assets. To record, make an entry crediting the accumulated amortization-patent account for the amount of the amortization. Alternately, many companies simply choose to credit the patent account directly for the amount of the amortization.
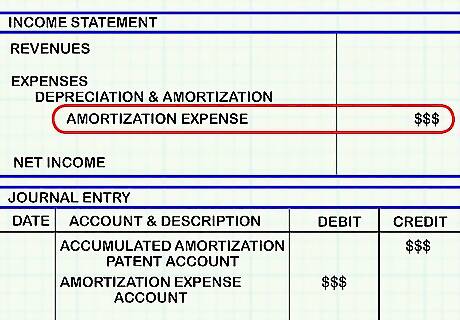
Record the amount that is amortized per year on the company's income statement. This is called "amortization expense" and is considered a cost of doing business that is subtracted from revenue. It is usually included under the "depreciation and amortization" line item. An equivalent debit to the credit made in the last step should be made to the amortization expense account (in both cases).

Keep good records. You should keep documentation of all invoices, patent grants, costs of research and development, and anything else relating to the value or useful life of the patent for at least seven years for future audit purposes. Note the dates that all patents were acquired and the cost for each.




















Comments
0 comment