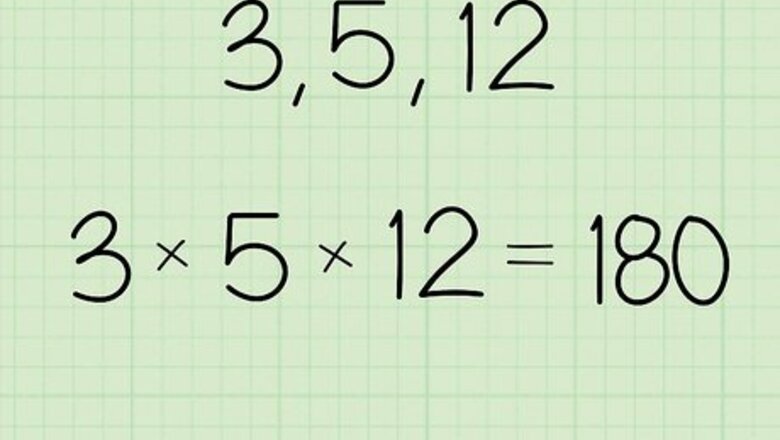
views
Finding the Geometric Mean of a Value Set
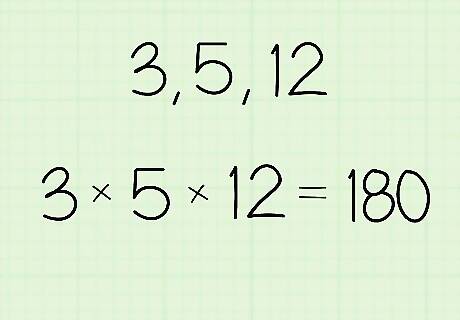
Multiply the values you want to find the geometric mean for. You can either use a calculator or do the math by hand when you find the product. Multiply all of the numbers in the set you’re calculating so you can find the product. Write down the product so you don’t forget it. For example, if the value set is 3, 5, and 12, then you would write: (3 x 5 x 12) = 180. For another example, if you want to find the geometric mean for the set 2 and 18, then write: (2 x 18) = 36.
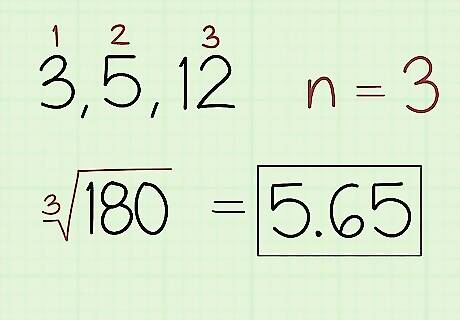
Find the nth root of the product where n is the number of values. Count how many values are in the set you’re calculating the geometric mean for the value n. Use the n value to determine which root you need to take of the product. For example, take the square root if you have 2 values, cube root if you have 3 values, and so on. Use your calculator to solve the equation and write down your answer. For example, for the set of 3, 5, and 12, write: ∛(180) ≈ 5.65. In the second example with a set of 2 and 18, write: √(36) = 6.Variation: You can also write the value as an exponent 1/n if it's easier to type in your calculator. For example, for the set 3, 5, and 12, you can write (180) instead of ∛(180).
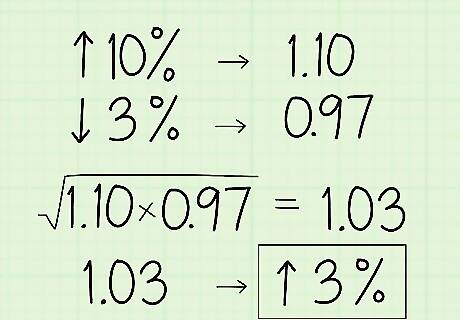
Convert percentages to their decimal multiplier equivalents. If the number set is written out as increases or decreases in percentages, avoid using the percent value in the geometric mean since it will skew your results. If the percent is an increase, move the decimal point 2 spaces to the left and add 1 to it. If there’s a percent decrease, then move the decimal point 2 places to the left and subtract it from 1. For example, say you want to find the geometric mean of the value of an object that increases by 10%, and then falls by 3%. Convert 10% to a decimal and add 1 to it to get 1.10. Then convert 3% to a decimal and subtract it from 1 to get 0.97. Use the 2 decimal values to find the geometric mean: √(1.10 x 0.97) ≈ 1.03. Convert the number back to a percent by moving the decimal point 2 places to the right and subtracting 1 from it to find a total of a 3% increase in value.
Calculating Geometric Mean with Logarithms
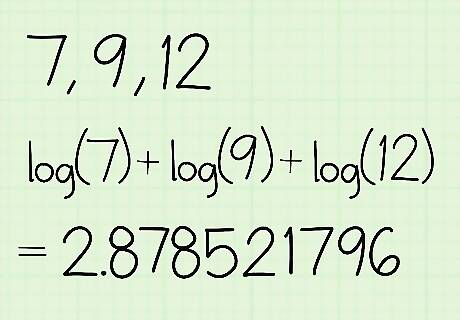
Add the logarithmic values for each number in the set. The LOG function takes a value out of base-10 and determines how many times you need to multiply 10 together to equal that value. Locate the LOG function on your calculator, which usually is on the left side of the keypad. Click the LOG button and enter the first value in the set. Type in a “+” before putting in LOG for your second value. Continue separating the LOG functions for each value with a plus sign before finding the sum. For example, with a set of 7, 9, and 12, you would type in log(7) + log(9) + log(12) before hitting “=” on your calculator. When you solve the functions, your sum will be about 2.878521796. You may also calculate each of the logarithms separately before adding the answers together.
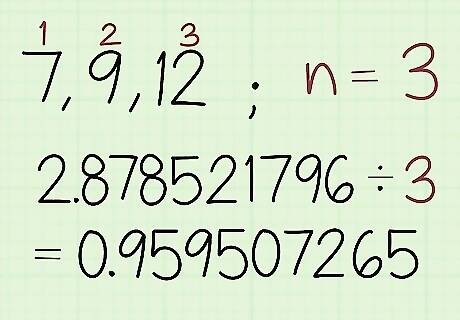
Divide the sum of the logarithmic values by the number of values in the set. Count the number of values in your set and then divide the sum you just found by that number. The answer you get will be the logarithmic value of the geometric mean. In this example, there’s a set of 3 numbers, so type in: 2.878521796 / 3 ≈ 0.959507265.
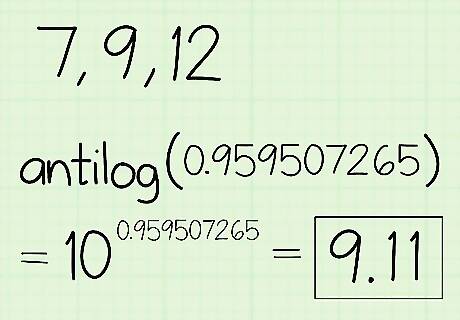
Take the antilog of the quotient to determine the geometric mean. The antilog function is the inverse of the LOG function on your calculator and it converts the value back to base-10. Look for the symbol “10” on your calculator, which is usually a secondary function of the LOG button. Press the “2nd” button in the top left corner of the calculator followed by the LOG button to activate the antilog. Type in the quotient you found in the last step before solving the equation. For this example, your calculator will read: 10 ≈ 9.11.



















Comments
0 comment