views
- Avoid irritating or rubbing the cyst, even while bathing—try a sitz bath or a gentle soak in the tub to keep the area clean.
- Use home remedies like an apple cider vinegar soak or warm compress to soothe the cyst.
- Take OTC pain relievers to help with any pain or discomfort.
- See a doctor if you experience pain or other symptoms of infection, like tender lumps, redness or swelling, painful intercourse, or a fever.
Diagnosing and Monitoring the Cyst
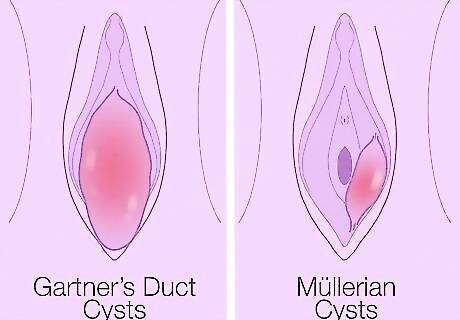
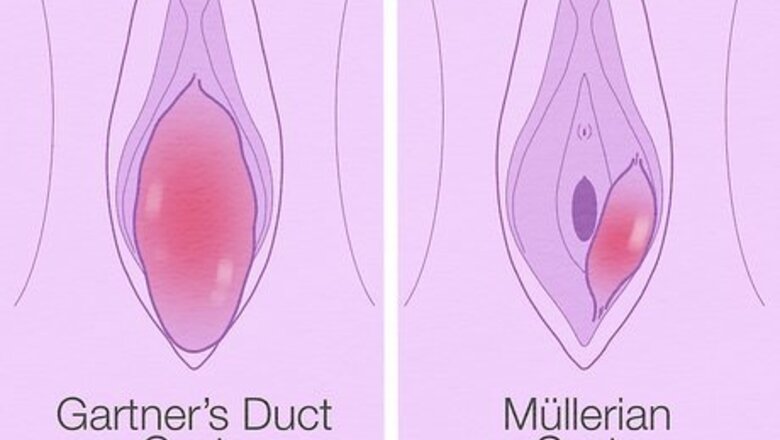
Consider what kind of cyst you have. Most vaginal cysts are called inclusion cysts. These small, painless cysts usually go unnoticed and clear up on their own. If you have cysts that you can see on either side of your vaginal opening, you may need to get rid of a Bartholin's gland cysts. Normally, the glands secrete fluids that lubricate the vaginal lips and opening. But, these can become blocked, creating fluid-filled cysts. Less common types of cysts that develop inside the vagina include: Gartner's duct cysts: these form during fetal development and they should disappear after birth. If cysts develop later in life, an MRI is usually needed to diagnose them. Mϋllerian cysts: these develop from fetal structures that should disappear after birth, but often don't. These cysts are filled with mucus and can develop anywhere inside the vaginal walls.
Watch for signs of an infection. While most cysts won't cause any discomfort, you may notice signs that the cyst has become infected. It's important to pay attention to these symptoms so you can get immediate medical attention. Signs of infection include: A lump near the vaginal opening that is tender or painful Redness and swelling around the lump Discomfort when walking or sitting Painful intercourse Fever
Call your doctor if the cyst is infected or painful. Book a gynecology exam or contact your primary care doctor. A normal bacterial infection or sexually transmitted infection can make the cysts uncomfortable. Let your doctor know if you have recurrent cysts, even if home treatments work. Recurrent cysts might need to be surgically treated. Look for symptoms of STIs, like painful urination or pain during intercourse. If you're over 40 years old and have Bartholin Gland cysts, you need to have the cysts removed. Your doctor will probably want to have it tested for cancer, though cancer is extremely rare in a Bartholin gland.
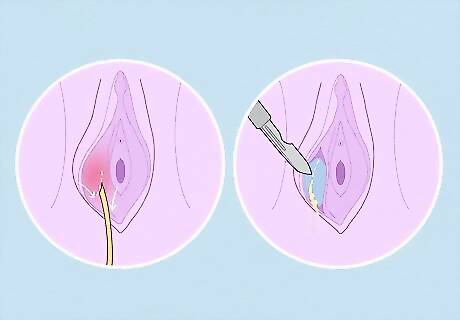
Follow your doctor's treatment recommendation. In addition to testing the cyst for cancer, your doctor may want to treat infected cysts. Treatment can involve draining the Bartholin's cyst by making an incision, then keeping it open with sutures or packing, which will be removed after a few days. A tube may also be used to drain the cyst. Your doctor may want to surgically remove a cyst if it returns, is large, or is painful. Remember that most vaginal cysts don't need treatment. Instead, they can reabsorb on their own. If they don't resolve on their own, these typically cysts remain small and painless.
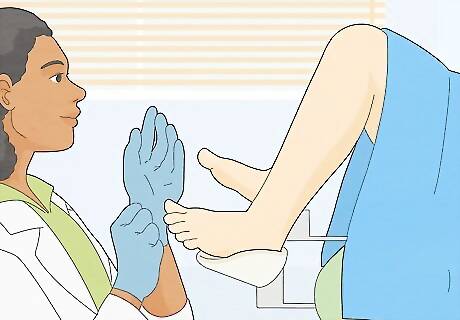
Get regular gynecological exams. If you have a cyst removed, have the area checked periodically to see if the cyst returns. It's a good idea to be in the habit of getting regular gynecological exams anyway. These can catch cervical cysts and cancer early. The American College of Physicians recommends that women of average risk for cervical cancer get pap smears and exams according to this new schedule: Ages 21 to 29: once every 3 years Ages 30 to 65: once every 3 years (or an HPV and Pap smear every 5 years) Over age 65: none are needed if recent tests come back normal
Home Remedies

Soak in a sitz bath to reduce swelling. Fill the sitz bath with warm water and place it over the toilet. This will allow you to sit and soak just your genital area. Add 1 to 2 tbsp (14 to 28 g) of Epsom salt in the water, then stir it until the salt dissolves. Sit on the bath for 10 to 20 minutes twice a day for 3 to 4 days. If you don't have a sitz bath, just run a few inches of water in your bathtub.
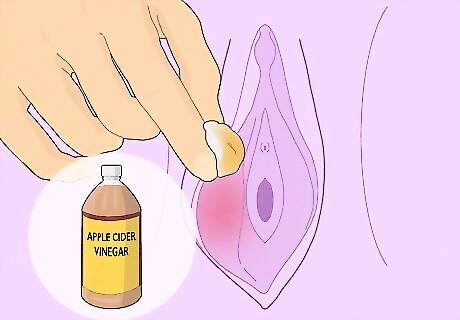
Use an apple cider vinegar (ACV) soak. More research is needed, but ACV can be used to try to reduce the size and swelling of vaginal cysts. Either run a sitz bath and add 1 cup of ACV or you can soak a cotton ball or swab with ACV. Apply the soaked cotton ball or swab directly to the cyst and hold it there for 30 minutes twice a day until you notice swelling reduce. While ACV is a popular home remedy, scientists caution against relying on vinegar as a medicinal treatment. Always consult your doctor before trying home remedies.
Use a warm compress. Fill a hot water bottle with hot water and wrap it in a clean towel. Place this against the cyst to provide some pain relief. Take care not to burn the delicate tissue in the vaginal area. You can also dip a flannel or cotton cloth in hot water, wring the water out, and apply it directly against the cyst.
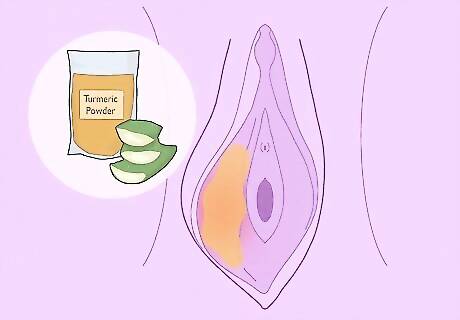
Apply an aloe vera and turmeric mixture to the cyst. Mix 1 to 2 tbsp (14 to 28 g) of aloe vera gel with 1/4 to 1/2 tsp (1.42 g to 2.8 g) of turmeric powder. Stir until the mixture forms a paste. Use a cotton ball, tampon, or swab to apply the mixture to the cyst. Leave it on for 20 to 30 minutes once a day. Don't rinse or clean off the paste; just let it run out naturally. Wear a pad so that the bright turmeric doesn't stain your clothing. Studies have shown that turmeric (curcumin) is an anti-inflammatory. This can reduce the irritation caused by vaginal cysts. However, if you experience any pain or discomfort, stop using this mixture immediately.
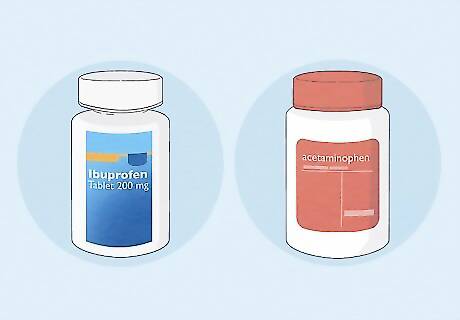
Take over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers. Since it may take a few days for the cyst to clear up, try OTC pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. If you feel severe pain that doesn't go away after taking OTC medications, contact your doctor. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding dosage and how often to take the medication.
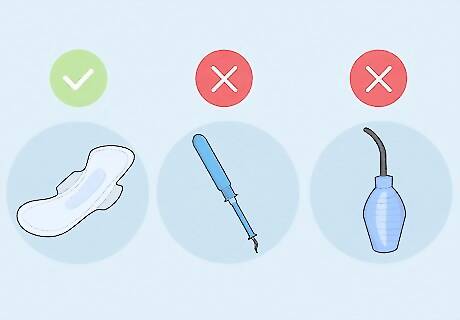
Avoid irritating the cyst. Never rub the cyst, even when cleaning or washing the area. Gentle soaks in the sitz bath or tub are enough to keep the area clean. Never douche, as douching is unnecessary, can irritate the cyst, and is considered to be harmful to your health in general. Since you'll want to avoid irritating the cyst, consider using a pad instead of a tampon if you're menstruating.



















Comments
0 comment