views
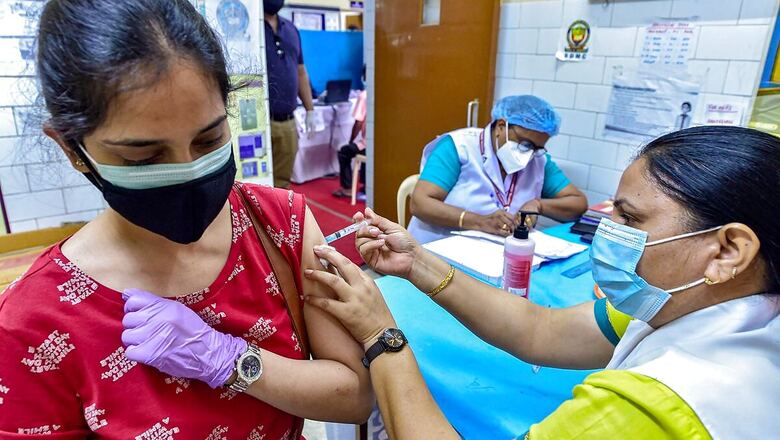
Niti Aayog member (Health) Dr VK Paul outlined on Thursday a plan involving eight vaccines that could help India inoculate all its citizens by the end of the year. The number is a significant jump from the two shots currently in use in India, which is faced with a devastating second wave of Covid-19.
In less than a year since the covid-19 outbreak began, hundreds of vaccine candidates have entered various phases of pre-clinical and clinical trial stages. According to the Covid-19 Vaccine Tracker, there are 115 candidates and 14 approved vaccines.
In India, two vaccines, Hyderabad-based Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin and Oxford-AstraZeneca’s Covishield, are currently being administered in a nation-wide vaccination drive. Russian anti-Covid vaccine Sputnik V is likely to be available by next week.
The government has given a push to increase vaccine manufacturing and has issued emergency use authorisation to Biological E, Zydus Cadila, Serum Institute of India for Novavax, Bharat Biotech’s nasal vaccine, Gennova and Sputnik V.
In a major push towards vaccine manufacturing and availability, Paul in a press briefing said, 216 crore vaccine doses would become available for the national vaccination drive. “Overall, 216 crore doses of vaccines will be manufactured in India between August and December, for India and for Indians. There should be no doubt that vaccines will be available for all as we move forward,” he said.
VACCINES IN INDIA AND THE PLATFORMS USED
Covaxin: Bharat Biotech partnered with the National Institute of Virology (NIV) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for the inactivated coronavirus vaccine Covaxin. Trial results have showed the vaccine has an efficacy of 78 per cent. Pathogens (viruses or bacteria) that cannot multiply can be injected into the arm without causing covid-19 inside the body. Using chemicals like formalin, the vaccine works by teaching the immune system to make antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Inactivated viruses are mixed with a tiny amount of an aluminum-based compound called an adjuvant which stimulates the immune system to boost its response to a vaccine. Atleast 55 crore doses of Covaxin would be available by December, the government said.
Biological E: Hyderabad-based pharmaceutical company Biological E Limited (BE) received emergency authorisation for its protein subunit BECOV2A vaccine. Rather than injecting a whole pathogen to trigger an immune response like in Covaxin, subunit vaccines (sometimes called acellular vaccines) contain purified pieces specially selected for their ability to produce a strong and effective immune response. Because these fragments are incapable of causing covid-19, subunit vaccines are considered very safe. Such vaccines are also relatively cheap and easy to produce, and more stable than those containing whole viruses or bacteria. Biological E is expected to produce 30 crore doses between August and December.
Covishield: The University of Oxford partnered with the British-Swedish company AstraZeneca developed a vaccine based on the viral-vectored platform. The Serum Institute of India is manufacturing the vaccine known as Covishield in India. Viral vector-based vaccines don’t actually contain antigens but rather use the body’s own cells to produce them. It uses modified virus (the vector) to deliver genetic code for antigen in the case of COVID-19 spike proteins found on the surface of the virus, into human cells. Various viruses have been developed as vectors, including adenovirus (a cause of the common cold). The coronavirus spike protein gene gene is added to two types of adenovirus, one called Ad26 and one called Ad5, to enable them to invade cells but not replicate. Once infected, the cells make large amounts of antigen, triggering an immune response against the virus. The Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine uses a chimpanzee adenovirus because humans will not have pre-existing antibodies to this adenovirus. However, there are human adenoviruses as well. But the risk here is that previous colds or infections in an individual may leave them with antibodies to the human adenoviruses, interfering with the vaccine. Over 75 crore doses will be made available by the SII between August and December.
Sputnik V: Russian Ministry of Health’s Gamaleya Research Institute developed a non-replicating viral vector coronavirus vaccine Sputnik V. The two-dose vaccine has an efficacy rate of 91.6 per cent. Sputnik V uses two human adenoviruses Ad5 and Ad26, the adenoviruses bump into cells and latch onto proteins on their surface. Once injected into the body, these vaccine viruses begin infecting our cells and inserting their genetic material – including the antigen gene – into the cells’ nuclei. Human cells manufacture the antigen as if it were one of their own proteins. At least 15.6 crore doses will be available in India by December.
Zydus Cadila: Ahmedabad-based pharmaceutical firm Zydus Cadila will be rolling out its plasmid DNA vaccine ZyCoV-D for rollout in India. Nucleic acid vaccines use genetic material from a disease-causing virus or bacterium (a pathogen) to stimulate an immune response against it. The vaccine genetic material orders instructions for making a specific protein from the pathogen, which the immune system will recognise and trigger a response against the virus. Zydus Cadila will be providing the Indian government 5 crore of its vaccine for the inoculation drive by December.
Novavax: The United State-based vaccine maker Novavax in partnership with vaccine manufacturer Serum Insititute of India will be rolling out the protein subunit covid-19 vaccine NVX-CoV2373 named Covovax. Like the Biological E candidate, the vaccine is protein subunit and works by teaching the immune system to make antibodies to the spike protein. Once vaccinated, the infected cells put fragments of its spike protein on their surface after a coronavirus is detected. Antigen-presenting cells activate a type of immune cell called a killer T cell before multiplying inside the body. The antibodies can also lock onto the spike proteins and stop the coronavirus from entering cells. The health ministry said the Serum Institute of India will provide 20 crore doses of Novavax by December.
Gennova: Pune-based Gennova Biopharmaceuticals has been approved for rollout of its indigenous mRNA vaccine in India’s vaccination drive. The Indian government has said Gennova will make available 6 crore doses by December. The vaccine uses messenger RNA (mRNA) carrying the genetic sequence for building the spike protein. Since the body’s natural enzymes would break down the mRNA molecule, it is wrapped in oily bubbles made of lipid nanoparticles. This resembles cell membranes and can deliver the RNA into the host cell, where the messenger RNA is treated like it belongs to that cell. Thereafter, the cell uses its protein-producing machinery to read the message and make spike protein, which is then released from the host cell and recognised by the immune system, triggering a response that results in antibody production and cellular immunity.
Intranasal: Bharat Biotech proposed an adenovirus vectored, intranasal vaccine for covid-19. A modified version of a adenovirus can enter human cells in this vaccine but not replicate inside blocking the infection. A gene for the coronavirus vaccine ads into the adenovirus DNA, allowing the vaccine to target the spike proteins that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter human cells. The ministry has ordered 10 crore doses of the intranasal vaccine for its vaccine drive.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Telegram.













Comments
0 comment