
views
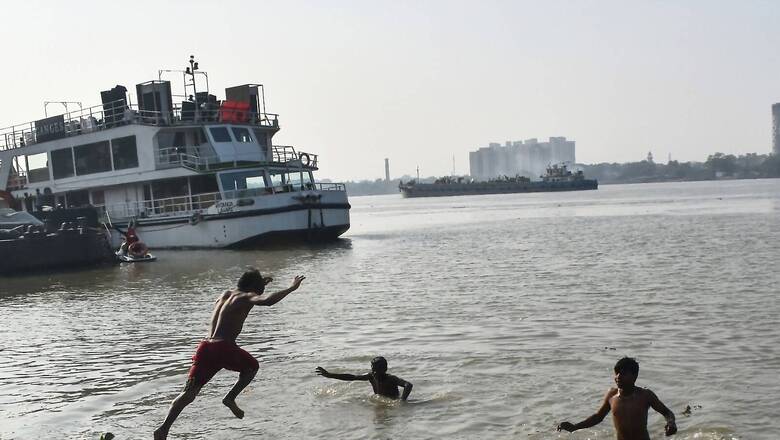
The Centre is planning to set limits for the minimum flow of water in various Ganga tributaries like Yamuna to have uninterrupted flow, which will ensure its cleanliness, a senior official said. In 2018, the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) released the e-flow notification for Ganga, which refers to the quality, quantity and timing of water flows required to maintain the components, functions, processes, and resilience of river ecosystems that provide goods and services to people. On the same lines, the NMCG is now planning to set limits for the minimum flow of water in various Ganga tributaries like Yamuna to have uninterrupted flow to ensure its cleanliness, NMCG Director General Rajiv Ranjan Mishra said.
"Setting minimum flow of water has helped us maintain an incessant flow of river Ganga. Further, to maintain the minimum flow of Ganga tributaries such as Yamuna and other rivers, the NMCG is in the planning stage to provide technical and analytical support by carrying out a detailed evidence-based assessment of the environmental flows, where significant flow regime modification has occurred post human interventions," he told PTI. Mishra said the planned intervention is in the proposal development stage for taking up study towards assessment of environmental flows in critical reaches of small rivers and tributaries of the Ganga river system.
He further said that the NMCG is working to enumerate the floodplains within 10 km of river Ganga by creating the inventories and developing integrated basin management plan to promote recharging groundwater and other waterbodies, which will ultimately contribute towards cleaning and maintaining continuous flow of Ganga river. The wetlands are considered to be an intrinsic part of the Ganga Basin and it is important to protect, conserve and rejuvenate them for the holistic development of Ganga river. The wetlands serve as the natural treatment system, which removes the toxic substances to drain into the river system, along with this it acts as a carbon sink, habitat for biodiversity and aquatic life and maintains the flow of rivers, which keep them alive. "Within the NMCG programme, the wetlands are approached by distinguishing them in two categories i.e., floodplain wetlands and urban wetlands. The floodplain wetlands are the ones found closer to the rivers and urban wetlands are those existing in cities or urban areas. The urban wetlands are usually in more danger due to encroachment and construction being done at the wetland sites," Mishra said.
He said to manage the urban wetland, the NMCG collaborated with the School for Planning and Architecture (SPA) to develop a toolkit for local stakeholders — 'Urban: Wetland Management Guidelines'. The toolkit has showcased the Bhagalpur Wetland case of lost waterbodies over the decades and how it relates to other rivers such as Champa river. The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has circulated the toolkit for guiding urban managers of all the cities and rivers situated at the bank of rivers or lakes, he added. Mishra said the NMCG is working with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare for scaling-up organic farming and agroforestry in Ganga states to boost farmers' income, improve water use and crop diversification. "Actions have been taken to cover organic farming, horticulture, agroforestry, and water conservation in a five-km area along the Ganga Basin and planned to cover approximately two lakh of hectares in the next five years. "In phase I, the total land covered for organic farming across the basin states was 23,840 hectares, which has been increased to 1,03,780 hectares. In phase II, the organic farming interventions are expected to benefit more than 18 lakh farmers in the Ganga Basin states," he added.
.
Read all the Latest News , Breaking News and IPL 2022 Live Updates here.
















Comments
0 comment