
views
Speaking Concisely

Plan before you speak. Choose what you want to say before you say it. This will help you convey the most important points without beating around the bush. If you are giving a speech, write out a script and stick to it. If you are speaking off the cuff, take a brief moment to plan out the most important parts of what you want to say. Think about how you would say something if you only have a few minutes. What do you need to include? What can you leave out? For example, if you are giving a project update in a meeting, you probably don’t need to discuss all of the steps you took to work on something. Instead, talk about the results that you’ve achieved on the project so far.

Know your audience. It’s important to know who is listening to you speak. This will help you determine how much explanation you need to give, or how you can cut corners. For example, if you are talking with a colleague who understands your work, you don’t need to spend a lot of time explaining basic concepts. If you are speaking to a crowd who is unfamiliar with your work, you might need to describe more.

Convey the central idea first. Start your talk with the most important idea. Give your audience the main headline of what you want to say. This also helps your audience follow your line of thinking. Your most important point won’t get lost. People tend to listen most closely to the first 30 seconds of a speech, so make this first part count.

Skip unnecessary details. Think about the details that the listener needs to know. Unless it is directly relevant, the listener probably doesn’t need to know the life history of someone in your story, or the color of a dog’s collar. Leave out these types of details.

Use active descriptions. Choose meaningful words that say a lot. Stay away from passive sentence constructions, such as “There are” and “We have.” Make declarative statements that get to the point immediately. Choose ways of speaking that pack a lot of meaning in fewer words.
Stay focused. Try not to get distracted when you’re speaking. Stay on topic without going off on a tangent about something not directly related to the topic at hand.

Pay attention to your speech. Start listening to how long it takes you to get to the point. This will help you start figuring out where you can trim words and tendencies from your speech. Then you can work on being concise. Do people often ask you to repeat yourself? Do you often use “What I mean is…” when speaking to clarify your points? Do you use words like “um” and “uh” a lot?

Practice speaking concisely. When you are confident with your speaking skills, you are more likely to speak concisely and directly. If you feel nervous or you lack confidence, your speech may start to fill with “ums” and “uhs.” Try practicing in front of a trusted friend. This person can give you feedback on your speech.
Writing Concisely

Plan out what you want to write. Wordiness or vagueness can occur when you're unsure of what you want to say. Avoid a lack of clarity by making an outline before you write. Pinpoint your main point and follow it with 3-5 supporting points.

Consider your audience. Think about who will read your writing. Write appropriately so that your audience will catch your meaning. For example, if you are writing something technical, consider the comprehension level of your audience. You may need to use space to explain concepts. If you write a letter to the editor, keep in mind that your letter may be trimmed down anyway. Don’t let your letter’s meaning get changed because the newspaper editor cut out half of your words.

Know your word limit. Most assigned written work has a word limit. This limit forces you to be concise. If you are not assigned a word limit, impose your own limit. Think about an appropriate length so that your reader won’t get bored.

Write in active language. Active language identifies meaning clearly and quickly in a sentence. People tend to understand active language more quickly. The active voice gives credit for action, declaring what happened. For example, instead of writing, “The cat was chased by a dog,” write, “The dog chased the cat.” You may still need to use the passive language in the event of delicate writing. For example, in this instance, “An error was made…,” passive wording softens the meaning.

Make each word serve a purpose. Choose your words carefully so that each word has a specific function. If you can just as easily leave out a word or phrase without changing your meaning, do so.
Use the two-line rule. The two-line rule refers to the length of your sentences. If your sentence takes up two or more lines on a sheet of paper (or typed on the computer), start looking at your phrasing to find unnecessary words. What can you cut out so that you convey the same meaning in one line? If you still need most of the information in the sentence, consider breaking it into two shorter sentences.
Editing Your Work

Eliminate unnecessary and redundant words. You may use more words than necessary to explain your idea. More often than not, these words are filler, taking up valuable space in your writing. Take out redundancy and extra explanations from your writing. Some typical filler words are: “just,” “some,” “that,” “but,” and “and then.” Rearrange phrases to the possessive form. You might use a phrase like “the leaves of the plant.” Rearrange this to the possessive form, writing “the plant’s leaves” instead. This retains the same meaning and eliminates two unnecessary words.
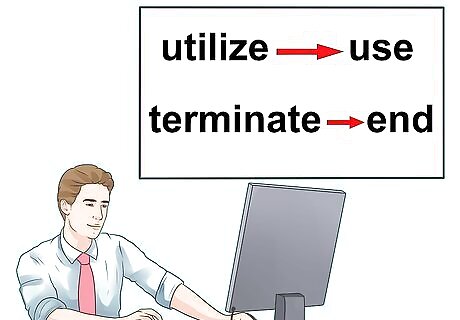
Replace wordy phrases with precise and concise words. Take out lengthy descriptions and replace them with more accurate words. For example, Say you wrote, "It is not the case that all historical kings, queens, and princes lived in very large and very beautiful castles." This can be shortened to: "Not all royalty lived in extravagant castles." Use a thesaurus to find a descriptive synonym for a general term. Don’t go overboard with choosing descriptors. In many cases, the simpler word or phrase is best. The reader will grasp your meaning more quickly. For example, replace “utilize” with “use,” or replace “terminate” with “end.”

Avoid excessive use of common modifiers. Some modifiers, such as "very" and "really,” are overused to the point where they have become dull and add no extra feeling to sentences. Eliminate many of these without changing the meaning of the sentence.

Print out a hard copy for editing. Go old school with your writing and work from a hard copy. It is satisfying to cross out unnecessary words with a red pen. See how much you can cut out without losing your original meaning.

Read your work out loud. Take a few minutes to listen for unnecessary words. Does the writing flow naturally as you say it out loud? Ask someone to listen to you reading your work. He might hear other unnecessary or redundant words that you don’t catch.
Practicing Concise Communication
Join Toastmasters. Toastmasters is an international organization that teaches and hones public speaking and leadership skills. You are given regular speaking assignments and will perform them in front of a supportive group. Search the Toastmasters website to find a local chapter.

Record yourself speaking. Listen to your speeches and presentations to catch instances of when you say “um,” “like,” and “uh.” Once you’re aware of these phrases, you will be more likely to eliminate them from your speech.

Get an editor. It may help to have someone else look at your writing. An editor can give you pointers on how to streamline your writing. This person is less attached to your writing and is more likely to suggest cuts that you might not make yourself.

Work on body language. When you have confident body language, you will be more confident in your speech. Confident body language include: Regular eye contact Holding your shoulders and back straight No fidgeting Smiling Relaxed muscles


















Comments
0 comment