views
Taking a Look at the Different Kinds of Hernias
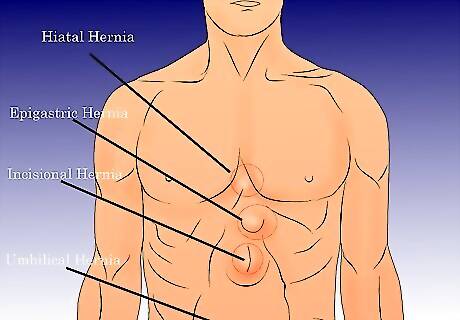
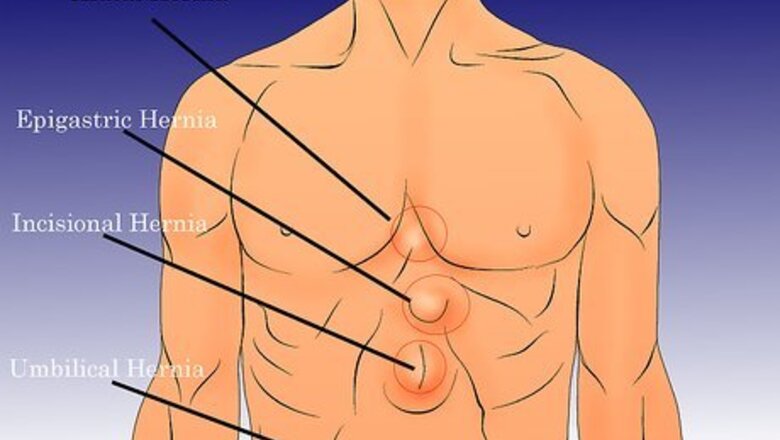
Check for hernias that occur around the stomach, abdomen, or chest. A hernia can affect different areas of your body in different ways, although a hernia in or around the stomach area may be the most common type of hernia. These hernias include: Hiatal hernia affects the upper part of your stomach. The hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm that separates the chest area from the abdomen. There are two types of hiatal hernia: sliding or paraesophageal. Hiatal hernias occur in people of both sexes, and are typically more common in people over the age of 50 and those who are obese. Epigastric hernia occurs when small layers of fat push through the belly wall between your breast bone and your navel. You can have more than one of these at a time. Although epigastric hernias often present no symptoms, it may need to be treated with surgery. Incisional hernia happens when improper care after abdominal surgery results in bulging through the surgical scar. Often, mesh lining is incorrectly installed and the intestines slip out of the mesh, causing a hernia. Umbilical hernia are especially common among infants. When the baby cries, a lump around the belly button area usually protrudes.
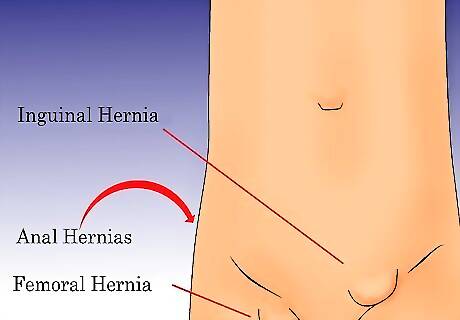
Know the types of hernias that affect the groin area. Hernias can also affect the groin, pelvis, or thighs when the intestines break out of their lining, causing uncomfortable and sometimes painful lumps in these areas. Inguinal hernia affects your groin area, and happens when a portion of the small intestine bulges through the abdominal lining. Surgery is sometimes necessary for inguinal hernias, as complications can cause life-threatening situations. Femoral hernia affects the upper thigh, right below the groin. Although it may present no pain, it looks like a bulge in your upper thigh. Femoral hernias are more common in women than in men. Anal hernia, or rectal prolapse, may cause the entire rectum to extend out of the anus, or may only push a part through. Anal hernias are rare and can affect anyone, but are more likely to be seen in older adults with a history of constipation or weak pelvic floors. They are often confused with hemorrhoids, but they are not the same thing.
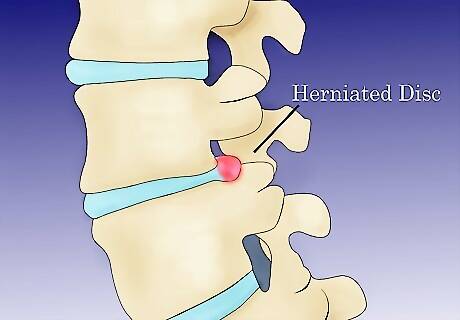
Understand the other types of hernias. Hernias can affect areas other than the stomach and groin region. In particular, the following hernias may present medical problems for individuals: Herniated discs happen when a disc in your spinal column pops out and begins to pinch a nerve. The disks around the spinal column are shock absorbers, but can be dislodged either by injury or disease, resulting in a herniated disk. Intracranial hernias, or brain herniation, occur inside the head. They happen when brain tissue, fluid, and blood vessels are moved away from their usual position in the skull, often after a head injury, stroke or tumor. Any brain herniation is a medical emergency and needs to be taken care of immediately.
Checking the Symptoms
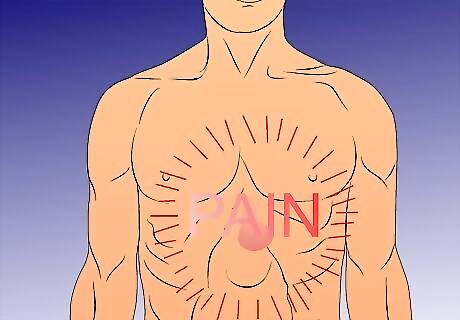
Investigate possible symptoms or signs of a hernia. Hernias may be caused by a host of different factors. Once they are formed, they may or may not present pain. Look for these symptoms, especially for hernias located in the abdominal or groin region: You see swelling where the pain is located. The swelling is usually on the surface of the areas such as the thigh, abdomen or groin.Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet1.jpg The swelling may or may not hurt.Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet2.jpg Bulges, such as those that you find in an inguinal hernia, can often be pushed back into your abdomen when you lie down. Bulges that cannot be pushed in when pressed down on need immediate medical attention.Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet3.jpg You may notice pain that ranges from mild discomfort to severe pain. A common symptom of hernias is pain present when straining or doing a strenuous activity. If you experience pain during the following activities, you may have a hernia:Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet4.jpg Lift heavy objects.Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet5.jpg Cough or sneeze.Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet6.jpg Exercise or exert yourself.Check for a Hernia Step 4Bullet7.jpg Hernia pain is often worse at the end of the day, or after long periods of standing.

Check with a doctor to confirm a hernia. Some hernias are what doctors called "trapped" or "strangulated," meaning that the organ in question loses blood supply or blocks intestinal flow. These hernias require immediate medical attention. Set up an appointment and meet with a doctor. Make sure to tell the doctor about all your symptoms. Undergo a physical examination. The doctor checks to see if the area increases in size when you're lifting, bending or coughing.
Know what puts you at an increased risk for hernias. Why do hernias affect more than 5 million Americans? Hernias can happen for many reasons, including straining on the toilet, chronic constipation, heavy lifting, and smoking. Here are a few more of the factors that put people at an increased risk for hernias: Genetic predisposition: If any of your parents had hernias, you are more likely to develop one.Check for a Hernia Step 6Bullet1.jpg Age: The older you get, the higher your chance of getting a hernia.Check for a Hernia Step 6Bullet2.jpg Pregnancy: While pregnant, the mother's stomach stretches out, making a hernia more likely.Check for a Hernia Step 6Bullet3.jpg Sudden weight loss: People who suddenly lose weight are at increased risk of developing a hernia.Check for a Hernia Step 6Bullet4.jpg Obesity: People who are overweight have higher chances of developing hernias compared to those who are not.Check for a Hernia Step 6Bullet5.jpg Persistent cough: Coughing puts a lot of pressure and stress on the abdomen, and can lead to a hernia.Check for a Hernia Step 6Bullet6.jpg















Comments
0 comment