views
Use strong, relevant keywords.
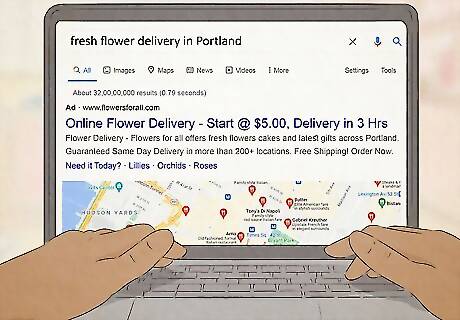
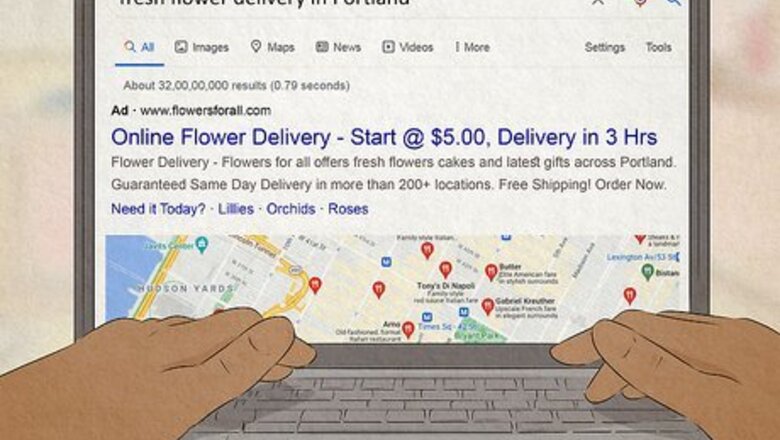
Keywords are popular words that people search for to find websites. Since keywords indicate helpfulness and relevance, search engines like Google give higher ranking to websites with keyword-rich content. Start by choosing primary keywords/phrases that reflect your business, services, content focus, and location. For example, if you sell flowers, a few good keywords/phrases might be: “flowers online,” “where do I buy flowers online,” and “fresh flower delivery in Portland." To find other strong keywords, try: Searching for similar products/topics. Then, look for common phrases in product names, descriptions, etc. Checking out related online forums. Read through post titles and popular discussions to find topics of interest. Using Google AdWords Keyword Planner tool. To search for new keywords, click “Discover new keywords.” Cross-check the relevancy of your current keywords by clicking “Get search volume and forecast.”
Incorporate keywords in a natural way.
Avoid “stuffing” each page with as many keywords as possible. At the end of the day, readability is more important than page visits—people won’t stay on your site if they don’t think the content is valuable. Insert your strongest and most relevant keywords a couple of times near the start of the page; use them sparingly anywhere else on the page that seems relevant. Keep in mind that keywords are most effective when you put them in titles, headers, the first paragraph of the article, and URLs. You won't be penalized for super common keywords and ordinary phrases like "San Francisco" or "macaroni and cheese." Search engines will penalize you (which affects visibility/ranking) if you repeatedly litter hyper-specific keywords on your web pages.
Add high-quality images and videos.

Images and videos make your content dynamic and attractive. This is true for all devices, but especially mobile users. If your site currently features big blocks of text and very few images on each page, consider streamlining the text and sprinkling in some high-quality images and/or relevant video content. A few things to keep in mind:
Most browsers support JPEG, GIF, PNG, BMP, and WebP image formats.
Use HTML image tags like or
Create quality content and refresh it weekly.
Well-written, fresh content keeps your audience coming back. It also encourages search engines to visit your site more often—if you’re consistently adding new keywords and content, you're always popping up in new and different search results. Try to add new content at least once a week. You might add a new product/service, a customer testimonial, updated images/videos, etc. Proofread text content on each page carefully—make sure it’s easy to read, organized, and error-free. Be sure to remove old content as soon as it loses relevancy. Adding a blog section to your website is a great way to include more engaging content. You can write entries yourself, rotate duties with various members of your staff, and/or ask guest bloggers to contribute.
Include links if they're helpful and relevant.

Use strong link text and aim to use mostly internal links. Link text is the visible text inside a link that users click on. Strong link text is specific—it makes it clear where each link will take your user before they click on it. The better your link text is, the easier search engines can “crawl” your site and find relevant information to display in search results. Avoid generic anchor text like "page, "article," or "click here.” To keep people on your site, focus mostly on using internal links (links that take users to other pages on your site). Try to avoid linking out to other websites unless it truly benefits your audience. If you do link out, only link out to authoritative sources.
Start a link-building campaign.

Reach out to relevant sites and ask if they'll link to your site. This is an easy way to start expanding your reach. Ideally, choose websites that are relevant to yours and have an established audience. Start by checking out each site carefully to make sure it's a good fit. Then, locate contact details on the page and email the site owner about possibly linking to you. For example: If you own a local deli and catering service, relevant sites you could reach out to include food bloggers, recipe websites, and party/event websites. Let them know that you'll be happy to link to them on your site, too! Think of this as a partnership.
Make sure the site looks good on all devices.

Content can look different and less accessible on a phone screen. Your site might look great on a desktop computer, but have you pulled up the site on your phone or tablet? Try viewing your website on a smaller screen and think about ways to improve the mobile experience. Developers can make a site mobile-ready by implementing: Responsive web design (recommended): This setup allows the server to send the same HTML code to all devices and alters the layout/appearance of each page to suit different screen widths, resolutions, etc. Dynamic serving: This setup allows the server to respond to different HTML on the same URL depending on the user's specific device (mobile, tablet, or desktop).
Go with a simple site structure.
A user-friendly site is appealing and boosts your visibility. You want your audience to navigate your site with ease, but a solid structure also enables search engines to “crawl” your site. Search engine bots and visitors should be able to easily find every page, figure out what each page is for, and navigate between them with ease. Here are some tips: Organize your site directory. Give each folder a clear purpose and name. Use keywords in URL structures (folder names). Make sure you can reach every page by starting at the home page. Add "breadcrumb navigation" at the top or bottom of each page so visitors can easily return to more general pages. For instance, a chocolate cupcake recipe might have breadcrumb links "Home → Baking → Cupcakes."
Give each page a short, unique title.
Include keywords in page titles for the most visibility. The page title (or title tag) is a brief description of each webpage. It shows up at the top of a browser window and in search results. Since page titles are one of the first things people see, they’re really important. Try to include a page-relevant keyword in every title tag and create a unique title for each page. Use 75 characters or less (including spaces) for each title. That's 6-9 words. If you're writing the HTML yourself, type in
Create concise, specific URLs.

The URL is the web address of each page on your site. Search engines use URLs to determine what each page is about and to accurately display relevant search results. Make your URLs clear, consistent, and keyword-rich. Avoid special characters, use hyphens to separate words (instead of spaces), and aim for 90 characters (including hyphens) or less for each URL. Example of a good URL: wikihow.com/making-websites/seo. Example of a vague/unclear URL: wikihow.com/directory7/hi-guys.
Write clear headers and organize them.
Headers organize information on the page in a clear, logical way. Organizing information with strong headers helps your audience find information quickly and easily. Additionally, search engines use your headers to analyze and rank content in search results, so they’re pretty important all-around! Make your headers brief, specific, and skimmable. A few things to keep in mind: Organize headers by importance. H1 headers are the most important and H6 headers are the least important. H1 headers appear in the largest, boldest font. Give every page an H1 header. Tag subheaders as H2, H3, etc. Keep headers under 70 characters. Begin each header with at least 1 keyword.
Insert accurate, keyword-rich metadata.

Meta description tags summarize the content on each page. They're one of the best tools for getting the right people to your site! Aim for descriptions that are helpful, accurate, and easy for visitors to read. Try to address the audience’s needs; think about why they might be clicking on each individual page. Use 1-2 complete sentences (50-160 characters) for meta descriptions. To add a description in HTML, type If you're using website or blog software instead of writing HTML, read the FAQs or contact customer service to find out how to add description tags.
Submit an XML sitemap to search engines.
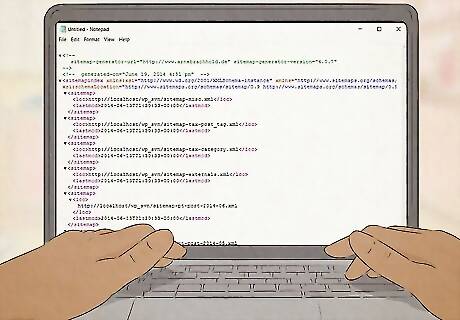
Sitemaps tell search engines what information is on your site. A sitemap is an organized list of URLs that helps search engines crawl your page efficiently. If you're a developer, you can make your own sitemap in XML format. If you're using a Content Management System (CMS) like Wordpress, it may have a tool on the dashboard that can generate the sitemap for you. You can also use a free sitemap generator website to create your XML sitemap. Then, submit the sitemap to search engines like Google, Yahoo, and Bing. You can submit to Google using Google WebMaster tools. If you’re using blogging software and there's no dashboard tool for this, you may be able to download a plugin to create your sitemap.
Use Google Search Console's Index Coverage report.
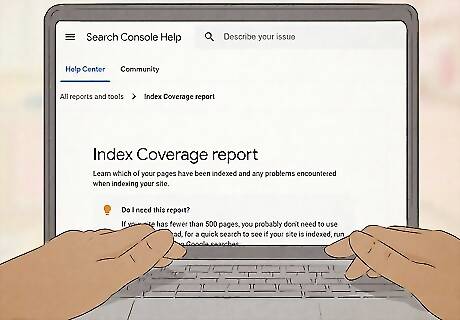
This free tool helps you track and improve how Google crawls your site. Once you submit a sitemap, it's important to monitor your site's "crawlability," especially as you add new content. Running a regular Index Coverage report helps you identify and fix crawlability issues that impact your ranking. This tool helps you do things like: Find and fix indexing problems. Request re-indexing of new or updated content. Get real-time alerts when Google finds indexing, spam, or other site issues. See Google Search traffic data. Track and troubleshoot mobile usability.
Use Alternative Methods to Drive Traffic.
There are other ways to drive traffic to your website. Once your website is finished and all set up, you can continue to optimize its reach by utilizing different methods. This can help spread the word about your website, helping it gain more popularity. A great method can be to issue a press release. Press releases help you by: Getting published on hundreds of news sites. Getting viewed by millions of readers around the world. Help you rank higher on Google.



















Comments
0 comment