
views
X
Research source
Humidity can affect your health, and it also determines which plants and animals can live in a particular environment. The amount of humidity also influences whether it will rain, snow, or be foggy. It is very difficult to measure and calculate humidity yourself without advanced equipment; however, there are a number of ways you can measure relative humidity by building a simple hygrometer with household items.
Measuring Humidity with a Hygrometer

Choose or make a hygrometer. Deciding which hygrometer to use depends on what you are using the humidity measurements for. If you are just curious about humidity in your home, you can make a very simple hygrometer using the wet/dry bulb thermometer system. If you need to accurately assess the humidity of your environment for preservation or scientific reasons, purchasing a proper hygrometer is a better idea. Consider the following questions before you purchase your hygrometer: Does it need to survive in extreme hot or cold temperatures? Does it need to run on battery power or will it be near a power outlet? Do you need an alarm to detect if the environment goes above or below a certain percentage of humidity? Is it easy to re-calibrate? Is it expensive? Does it require a lot of maintenance? Is it easy to understand and use?

Select a representative location for measurement. Once you have chosen your hygrometer, you need to pick a good location to keep it. Humidity measurements are dependent on temperature so choose a location that does not experience frequent temperature fluctuations. Place the hygrometer in a location that has a consistent temperature similar to the rest of the room. Avoid placing the hygrometer near doors, heaters, humidifiers, or air conditioners.
Acclimate the hygrometer to the environment. To get the most accurate readings, you must leave the hygrometer in your chosen location for a few hours so it can reach the ambient temperature of the environment. Taking a reading just after placement will likely result in an inaccurate reading.
Take regular measurements of humidity. If you are trying to determine if you have humidity fluctuations in your home, take readings every few hours or days. This will allow you to chart the humidity levels over time. Note that as air gets warmer, it can hold increasingly more moisture. The higher the temperature, the higher the relative humidity.
Calibrate the hygrometer, if necessary. Typically, a hygrometer needs to be calibrated about once a year. Calibration involves comparing the readings of your instrument to that of a calibrated reference sample and adjusting yours to match. Calibration is most important for scientific or research work. In this case, the hygrometer must be sent to a special facility for calibration. If you are using a homemade hygrometer, you can leave your hygrometer outside and check it against the reported readings for the day.
Measuring the Dew Point Experimentally[5] X Research source

Fill a metal can with water. The can should have a shiny surface to reflect light and heat away. Metal is the best material to use for this particular experiment. Fill the can about 2/3 full, leaving enough space to add ice cubes.

Add ice cubes, continuously stirring until condensation forms on the can’s surface. Add the cubes gradually, stirring the ice water mixture with a thermometer as you do so. This will keep the can surface the same temperature as the water. Continue adding ice, a few cubes at a time. Stir after each addition until the cubes have melted. Keep adding ice until you see water condense on the outside of the can.
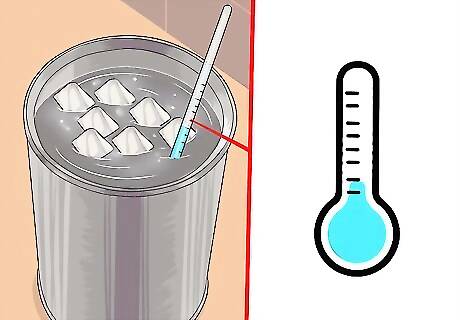
Read the temperature on the thermometer. This is the dew point temperature. The dew point is the temperature at which water completely saturates the air and water vapor condenses. The can and water are a simplified form of a chilled mirror hygrometer, a device with electronic sensors which meteorologists use to measure dew point. The higher the dew point temperature, the more someone will feel the moisture in the air.
Calculating the Relative Humidity
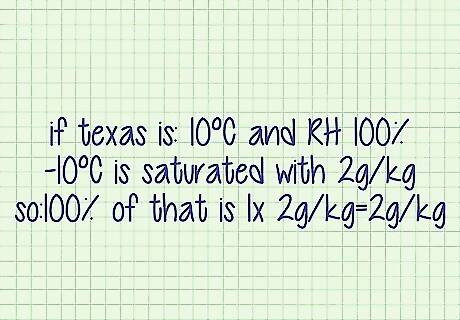
Determine how much water vapor is in the air. This can be expressed as the ratio of grams of water vapor to the number of kilograms of dry air. This is called the "actual mixing" ratio. This data can be obtained online as measured from instruments such as a microwave water radiometer. Measuring the water vapor in the air is not something that can be done with household items.

Determine how much water vapor the air can hold. This is the point at which the air would be saturated with moisture and is called the saturation mixing ratio. The amount of water vapor the air can hold is dependent upon the temperature of the air. Tables are available online that will tell you the capacity of water vapor at a specific temperature. The higher the temperature, the higher the water vapor capacity. To determine how much water vapor the air can hold at a certain temperature, reference the table at https://brownell.co.uk/datasheets/basics_humidity.pdf.

Divide the actual mixing ratio by the saturation mixing ratio. This simple calculation produces the relative humidity. Thus, if the air currently holds 20 grams of water per kilogram of dry air and can hold 40 grams of water per kilogram of dry air, the relative humidity would be 20/40, or 50 percent.

















Comments
0 comment