
views
X
Expert Source
Damaris Vega, MDBoard Certified Endocrinologist
Expert Interview. 11 November 2020.
If you are potassium-deficient, scroll down to Step 1 to find out how you can boost your potassium levels.
Eating Potassium-Rich Foods
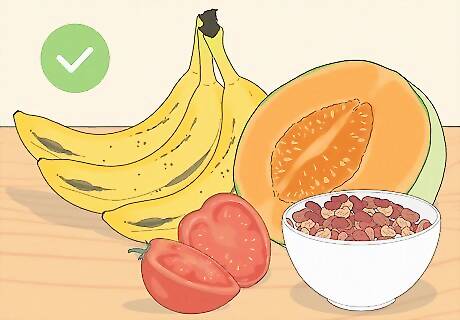
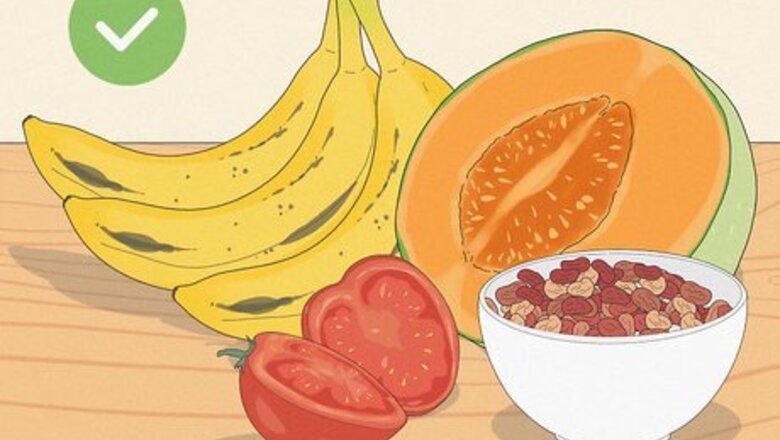
Eat fruits rich in potassium. As most people know, bananas are very rich in potassium. In fact, one banana contains 594 mg of potassium. However, there are other fruits that can help you restore your levels of potassium. These fruits include: Tomatoes (one small tomato can contain 900 mg of potassium), oranges, cantaloupe, strawberries, kiwis and the dried versions of apricots, peaches, prunes, and raisins.
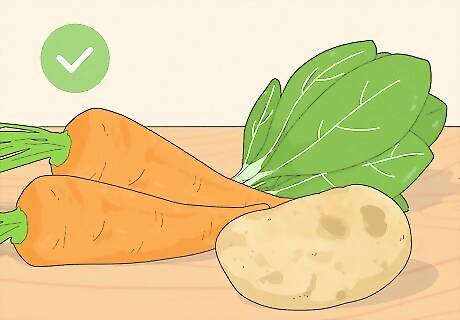
Consume some potassium-rich vegetables. Fruits are not the only great source of potassium. Vegetables can also give your potassium levels a boost. Veggies that will kick start your potassium intake include: Carrots (one cup of raw carrots contains 689 mg of potassium), potatoes, spinach and other dark, leafy greens, mushrooms, and acorn squash.
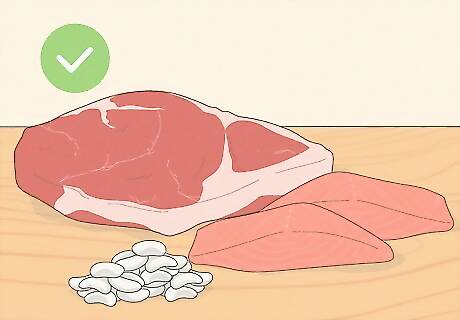
Eat sources of protein that are high in potassium. Salmon is one of the best proteins to eat when trying to restore your potassium levels. Three ounces of this fish generally contains about 319 mg of potassium. Lean beef and white beans are also excellent sources of both potassium and protein.
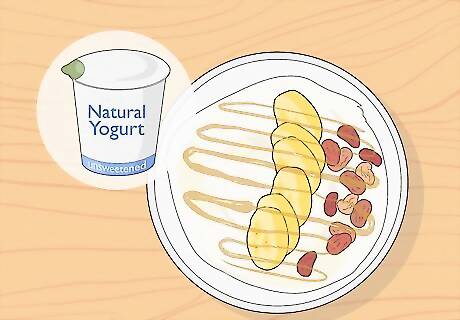
Combine some of these items for high-potassium meals. While eating all of these potassium-rich foods separately is great, making a meal out of them is even better. Try composing your meals so that they are as high in potassium as possible. Some meal ideas include: Yogurt (which is also potassium-rich) with bananas and raisins. Cooked salmon with sauteed mushrooms and a spinach salad. A snack of dried apricots and raw carrots.
Using Potassium Supplements
Consult your doctor before taking potassium supplements. If you are only mildly potassium deficient, eating potassium-rich foods should balance out your potassium levels. Once you have purchased potassium supplements, only take the prescribed amount--over compensating and taking more than the prescribed amount could lead to diarrhea, stomach irritation, and nausea and may cause muscle weakness, slowed heart rate, and abnormal heart rhythm.

Take potassium supplements in pill form. Extended-release form tablets are designed so that it will not dissolve in the stomach, but in the intestines. This extended release will help prevent the irritation of gastric lining. Potassium tablets should be taken with one full glass of water. Do not crush or chew potassium tablet as this will affect their extended-release feature.

Try a powdered or liquid form of potassium. You can purchase potassium powder or liquid that can be mixed with water and then drunk. For the correct dosage, you should follow the instructions provided by your doctor. Generally, powdered and liquid potassium must be completely dissolved in a ½ glass of water. If too much of this powder or liquid is consumed, it could cause gastric irritation.
Consider intravenous potassium. Taking potassium intravenously is strictly intended for extreme cases of potassium depletion and used under strict physician supervision. If you think your potassium levels are dangerously low, talk to your doctor about intravenous potassium. Do not try this on your own. Fast infusion may lead to cardiac irritation causing life threatening irregular cardiac rhythms.



















Comments
0 comment