views
WORLD ZOONOSIS DAY 2022: World Zoonosis Day is held annually on July 6, worldwide, to raise awareness about the infectious diseases collectively termed zoonotic diseases. The day is celebrated in memory of Louis Pasteur, a French biologist who, on July 6, 1885, successfully administered the first-ever Rabies vaccine to a patient named Joseph Meister.
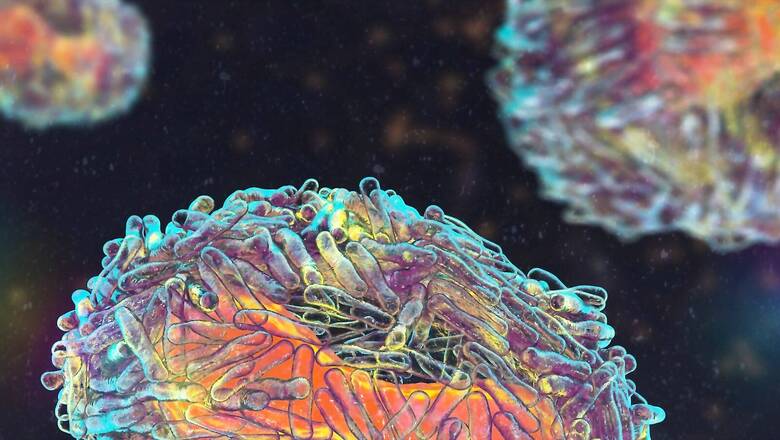
What is Zoonosis?
Zoonotic diseases originate in animals and can spread to humans. Infections occur through bites or contact with the infected animal’s bodily fluids. Virus, bacteria, fungi, prions or parasites cause zoonosis. Rabies, Ebola, certain strains of Swine flu, leptospirosis, brucellosis, anthrax, Zika and Ebola viruses, rickettsioses, plague, chikungunya, dengue and Japanese encephalitis, are the most notorious zoonotic diseases.
Zoonotic diseases were acquired by humans through hunting and consumption of wild animals initially and then through domestication. The diseases are endemic in tropical regions and are a risk factor in economically challenged and developing nations.
The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) in India publishes an annual report called ‘Zoonotic Diseases of Public Health Importance.’ The document provides detailed information on several zoonotic diseases and safety precautions for laboratory personnel handling such diseases.
Symptoms
Zoonosis symptoms include fever, muscle and joint pain, headache, diarrhoea and fatigue. These symptoms are also present in non-zoonotic ailments. Patients must not treat themselves at home but consult a doctor to get a proper diagnosis. Proper diagnosis of zoonosis is much lower in animals than in humans as the animal healthcare system is poorer and more expensive.
Treatment
Viral zoonosis is challenging to treat. Post-exposure sanitisation of the wound, vaccination, antiviral drugs, serum globulin and supportive therapy are some treatment options available. Herbal medicines and dietary polyphenols are the other treatment options. Bacterial zoonosis is treated with antibiotics such as fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, beta-lactams and macrolides.
Drug resistance, an emerging crisis, develops in bacteria from improper and repeated use of antibiotics, though. Many antibiotics used to treat zoonotic diseases no longer work because the pathogens have become resistant. This might make many such diseases untreatable in the future.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News, watch Top Videos and Live TV here.

















Comments
0 comment