views
A craving for sugar has always been attributed to a blood sugar imbalance in your body. If you crave sugary foods each time you have your meal, then you are in for serious health issues. In a recent study conducted by a team of researchers from IIT, Mandi, the insidious link between excess sugar intake and concomitant fatty liver disease, known as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in medical parlance, has been unravelled.
The team has identified the molecular link between sugar and fat accumulation in liver and alerted the public to the dangers of it. Now it’s on our hand to reduce sugar intake to stop NAFLD in its early stages.
Let’s get down to brass tacks and get our heads around what NAFLD is and what causes it:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
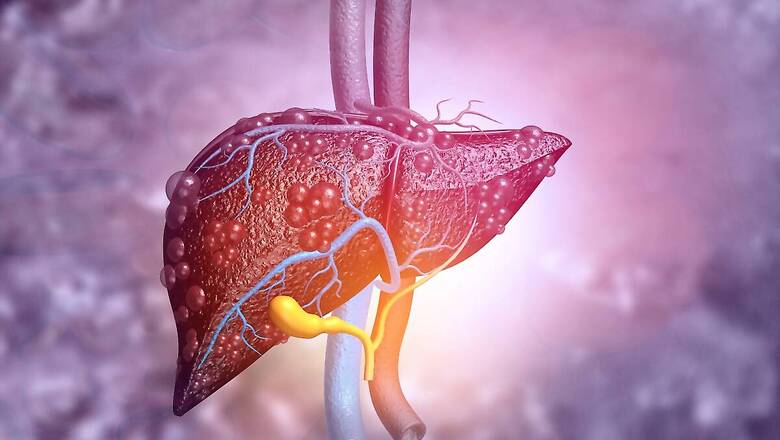
Simply put, NAFLD refers to a medical condition where there is accumulation of excess fat in the liver. The disease is so insidious that people under the grip of it remains unaware of having it as symptoms don’t show up in the early- to mid-stages. The accumulation of excess fat can irritate the liver cells, and if left untreated, can result in scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) and cause cancer in the long run.
What causes NAFLD
Overconsumption of sugar – both table sugar (sucrose) and other forms of Carbohydrates – is without doubt one of the many reasons that causes NAFLD. The consumption of excess sugar and carbohydrates causes the liver to convert them into fat through a process called hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis or DNL, says Dr. Prosenjit Mondal, associate professor, School of Basic Sciences, IIT Mandi.
According to the research team, the molecular link between sugar and fat accumulation in the liver would go a long way in developing therapeutics for the disease.
What the Study Found
The findings – published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry – indicate that the sugar-mediated shuttling of hepatic NF-KB p65 reduces the levels of another protein, sorcin, which in turn activates liver DNL through a cascading biochemical pathway, Mondal was further quoted.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here.
















Comments
0 comment