views
X
Trustworthy Source
United States Copyright Office
Part of the Library of Congress, responsible for maintaining copyright records
Go to source
Registering Your Copyright
Prepare your computer to use eCO. Most copyrights can be registered using the U.S. Copyright Office's electronic registration system, known as eCO. Before using eCO, you will need to make sure your computer is optimized to run eCO in order to avoid technical problems during the registration process. Adjust your settings as follows:: Disable your browser's pop-up blocker. Disable any third-party toolbars. Set your security and privacy settings to medium. The U.S. Copyright Office has tested the eCO system using the Firefox browser on the Microsoft Windows 7 Operating System, and advises that other configurations may result in less-than-optimal eCO performance.

Familiarize yourself with the eCO process. If you would like an overview of how to use the eCO system to register your copyright, take some time and read through the tutorial presentation offered by the U.S. Copyright Office. The tutorial will walk you through using the eCO system to file your copyright registration. A number of other sites provide step-by-step instructions on using the eCO system if you don't like the government's presentation.
Complete the eCO application. After you have familiarized yourself with the process, open the eCO portal and create an account. After doing so, click on "Register a New Claim" on the left-hand side of the welcome page, and follow the prompts to provide the necessary information for your copyright registration. As you complete the application, the steps on the left-hand side will get checked off. When all sections are checked, your application is ready to send. When you have entered and reviewed all information for accuracy, click "Add to Cart," The amount of your filing fee will be displayed on this window. Review the information, and then click "Checkout" to proceed to the payment step.
Pay the fee. You have several options for payment. First, you can enter your bank-account information and transfer the required funds electronically. Alternatively, you can pay with a debit/credit card. To do this, you will be directed to Pay.gov, a website operated by the U.S. Treasury Department that handles payment to government agencies.
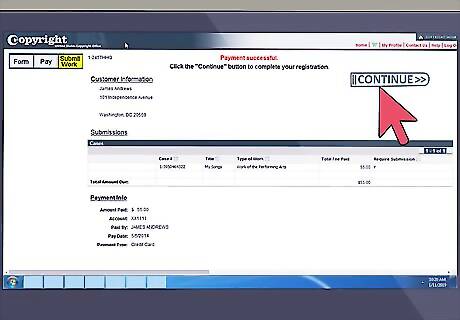
Deposit a copy of your work. The final step in this process is to send in a copy of the work being registered to the U.S. Copyright Office. Generally, you may only deposit a copy through eCO for works that are either (1) unpublished or (2) published only electronically. After paying the fee, click "Continue." You can upload an electronic copy on the following screen. If you have to send in a physical copy of your work, click "Create Shipping Slip" on the bottom of this screen, print the slip, attach it to the parcel, and send it to the address listed on the slip. If you are unsure of the deposit requirements for your particular piece of work, contact the U.S. Copyright Office.
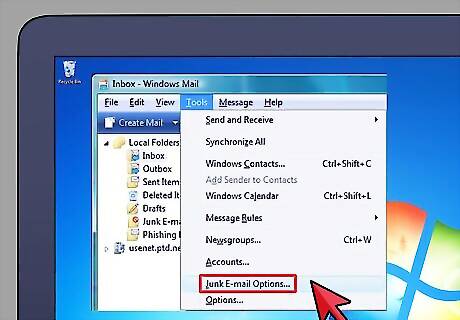
Review all correspondence you receive from the Copyright Office immediately. The Copyright Office may contact you by phone or e-mail about your application. If any additional documentation or information is required, you will be notified and should update your registration application as soon as possible. Check your spam folder to make sure you do not miss anything.
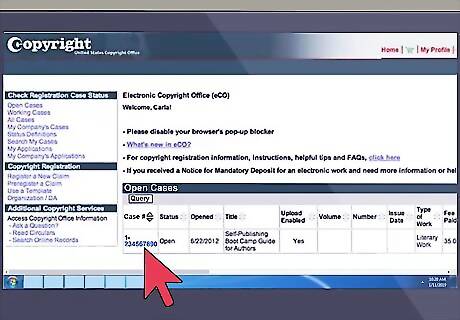
Follow up on your registration. To check the status of your application, log in to eCO and click on the blue case number associated with your claim in the “Open Cases” table at the bottom of the screen.
Understanding Copyright Registration
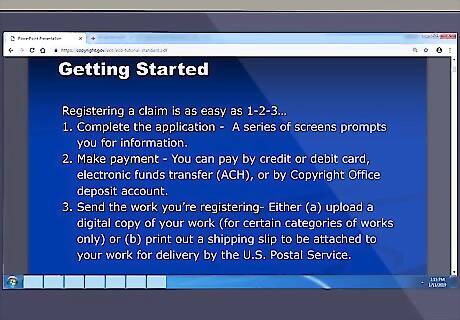
Understand the basic steps to register a copyright. Registering a copyright with the U.S. Copyright Office involves three basic steps: (1) complete an application either on paper or using the U.S. Copyright Office's eCO registration system; (2) paying a fee; and (3) depositing a copy of the work being registered with the U.S. Copyright Office. Once you complete these steps, your copyright will be officially registered.
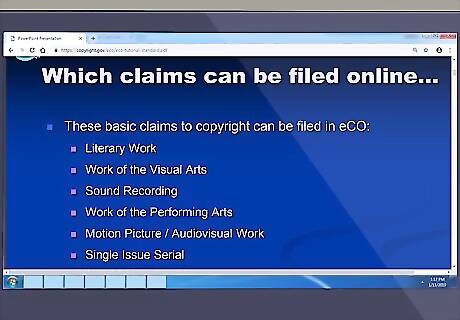
Know which types of work can be registered using eCO. If you can, you will want to use eCO to register your copyright because using this electronic system results in the lowest filing fee, the fastest processing time, the ability to track your submission online, and the ability to deposit certain works directly online without having to mail them in separately (and risk them getting lost, damaged, etc.). You can use eCO to register the following works: Literary Works Visual-Arts Works Performing-Arts Works Sound Recordings Motion Picture/Audiovisual Works Single-Serial Issues (e.g., a single issue of a magazine or newspaper) For detailed explanations of the above terms, consult the U.S. Copyright Office's guide explaining the different types of creative works.
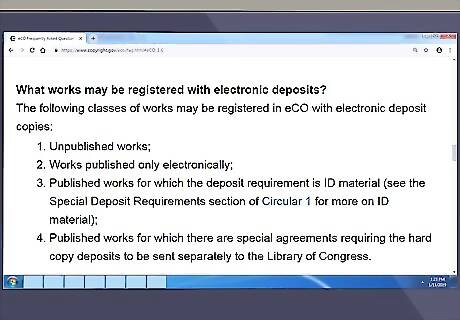
Determine if your work is published or unpublished. You will only be able to use eCO to register (1) any single work, (2) a collection of unpublished works by the same author, or (3) multiple published works in the same unit of publication (like a book of pictures). The publication status also determines whether or not you will be able to deposit a copy of your work electronically, or if you will have to mail in a copy to the U.S. Copyright Office. According to copyright law, a work is published if you have sold, rented, leased, or lent the work to the public. It is also considered published if you have offered copies to another party for purpose of further distribution, public performance, or public display.
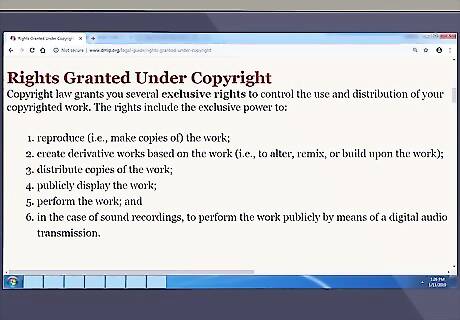
Know your rights. As the owner of a copyright, you have the exclusive right to do, or to authorize someone else to do, the following, subject to specific limitations: Reproduce the work. Create new works based on the original work by altering it, changing it to another form, or building on it in some way. (These are known as "derivative" works.) Distribute copies of the work. Publicly display or perform the work.

Learn about additional rights in visual arts. Subject to "fair use", an author of a work of visual art has additional rights of attribution and integrity, for his or her lifetime, including: The right to claim authorship and to prevent false attribution of authorship in other works. The right to prevent attribution of authorship for his or her works that have been mutilated or distorted in ways prejudicial to the reputation of the author. Certain limited rights to prevent the intentional destruction or mutilation of the work.
Protecting Your Work Online
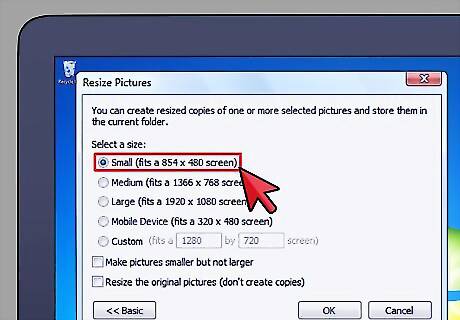
Upload low-resolution images. In the internet age, many artists use the internet to display or promote images of their work. If you plan on doing this, one way to protect against unauthorized use is to only upload low-resolution images of your art. This allows you to promote your work online by showing people what you've made, while at the same time preventing less-than-reputable individuals from obtaining clear, full-size copies.
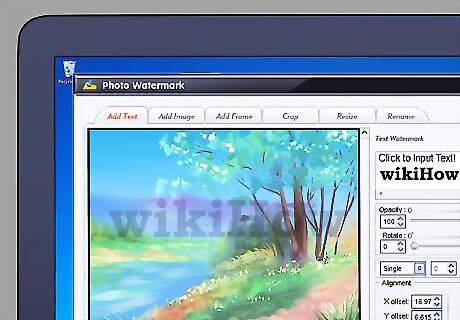
Watermark your images. Using an image editor, place a translucent mark identifying the work as yours conspicuously across the image. This way, anyone who obtains a copy will not be able to distribute it or use it freely without everyone who views it knowing where it came from. You can also consider adding your name to the filename when you upload an image. There are other technical measures for marking your digital files with searchable markers, and even for preventing any unauthorized copying or distribution, if you are willing to add the necessary restrictions on customer access.
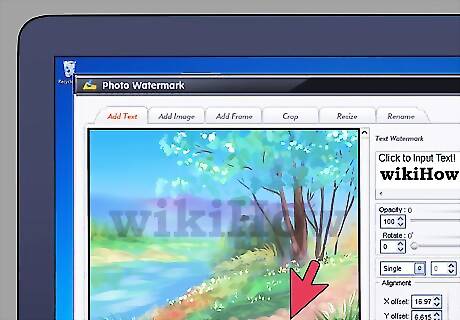
Add a copyright notice. You can also obtain a psychological protection of your works by placing a copyright notice on them in a corner or other discrete, yet clearly visible, space. Use the copyright symbol (©), followed by your name and the year the work was created. This should at least serve as a signal that the work is yours, and that you intend to protect it by the copyright that automatically triggered when you created the work.
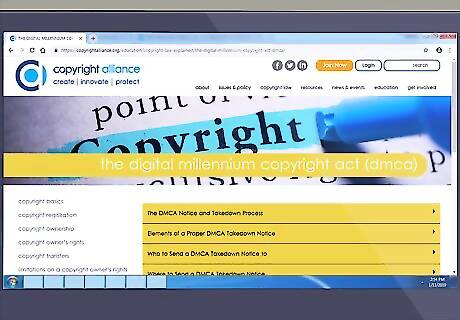
Pursue removal of unauthorized copies. Under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), the owner of a copyright may file an official notice for "takedown" of unauthorized copies being distributed on a server in the USA. The notice is sent to the "registered copyright agent" for the online service provider of the website and they must arrange for timely takedown of the works to avoid being sued. The online service provider is immune from lawsuit for infringement if they follow the required steps of DMCA. The works may be restored online if the service provider receives a proper counter-notification from the user who posted the allegedly infringing materials. You would then need to sue the user for a federal restraining order.

Register your copyright and sue infringers. Once you have discovered infringement, been unable to get them to stop with warnings and complaints, you may register your copyright (within one month) and sue for damages (including statutory damages), attorneys' fees, and a permanent injunction.




















Comments
0 comment