
views
Blockchain technology is all the rage these days in the technology world. Just in case you have never heard of this before, Blockchain is what powers the crypto-currencies, like the Bitcoin. While Bitcoin has been a hotly debated topic around the globe, its widespread popularity has largely been because of its involvement with money. But in case you think that Bitcoin is in itself a revolutionary technology, you are wrong on many levels. Primarily because it is not Bitcoin that translates into a ‘path-breaking technology’ but Blockchain. In essence, Bitcoin is a very small, but an important application of the Blockchain technology. Bitcoin IS NOT Blockchain.
So what is Blockchain? In very simple terms, blockchain is a ‘distributed ledger’ or a ‘distributed record’ that is used to keep a track of information transfer between points. Consider a monetary transaction between person A and person B. In the banking system prevalent today, it is the bank that keeps the transaction record between the two people. Now consider that an entire network of people has a record, containing all the transaction history amongst these two people (in an encrypted form of course). This shows the ‘distributed’ element of the blockchain.
So how is it better? It is simple. If the bank has its records deleted tomorrow for any reason, there will be no record of the transactions between person A and B whatsoever. Now consider the same scenario in a distributed ledger. If the records from any one system are deleted for any reason, there is a whole network of people having the same records as a backup. So essentially, the transactions that took place between person A and B will never be lost.
That is not the only plus of a distributed ledger though. It also helps secure the records, more than a centralised system. As an example, consider that a bank’s system is hacked in a cyber-attack. The hackers have to target only one system and approve the transactions from there in order to move the money to their account. However, in a blockchain, a transaction cannot be initiated until the time more than 50 percent of systems in that distributed ledger approve it. So to steal money in this scenario, the hackers would have to target more than 50 percent of systems for the same.
Now, this is just an overview of how the Blockchain technology works and its advantages. Let us dive a little more into the depth of this technology’s working. For this, let us first know how it all started.
Also read: After Nokia 5233 Tragedy, Here’s a List of Old Nokia Feature Phones You Shouldn’t Buy
A Brief History
Contrary to the popular belief, Blockchain technology was not invented by the creator of Bitcoin, a person or an entity identified as Satoshi Nakamoto. Instead, the first records of the technology have been traced back to 1991, in a paper published by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, titled ‘How to Time-Stamp a Digital Document’. As the title of the document suggests, this involved a use of cryptographic elements to time-stamp digital documents in such a way that they could not be tampered with.
Following its invention, the technology was left largely unused, i.e. until the time Nakamoto came into the picture. Like a scene straight out of a Hollywood sci-fi flick, Satoshi Nakamoto, the entity unknown to this date, published his/ her ‘White Paper’ explaining a new form of digital currency to the world, called Bitcoin. The ‘Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System’ used the Blockchain technology in its first conceptual appearance. Little was known at the time that the currency would spread like wild-fire in the following years and grow from being exchanged for a couple of pizzas for one unit to having a value of around Rs 4.5 Lakh for the same at the time of writing.
Along with the Bitcoin, spread the notion of Blockchain and the world started to realize its potential uses in areas other than digital currencies.
Elements of a Blockchain
Now we already know that a Blockchain is a distributed ledger. But what exactly are the elements that constitute a Blockchain? In essence, it is a ‘chain’ of ‘blocks’ that works here. So let us have a look at what each of the ‘block’ includes.
Inside a Block: On a very basic level, every block in a Blockchain comprises of three core elements:
1. Data inside the block
2. Hash or the unique identity of the block.
3. Hash of the previous block.
The ‘Data’ inside each block depends on the purpose for which the technology is being used. For instance, in a Bitcoin blockchain, the blocks contain the sender’s ID, the receiver’s ID as well as the amount of Bitcoins being transferred.
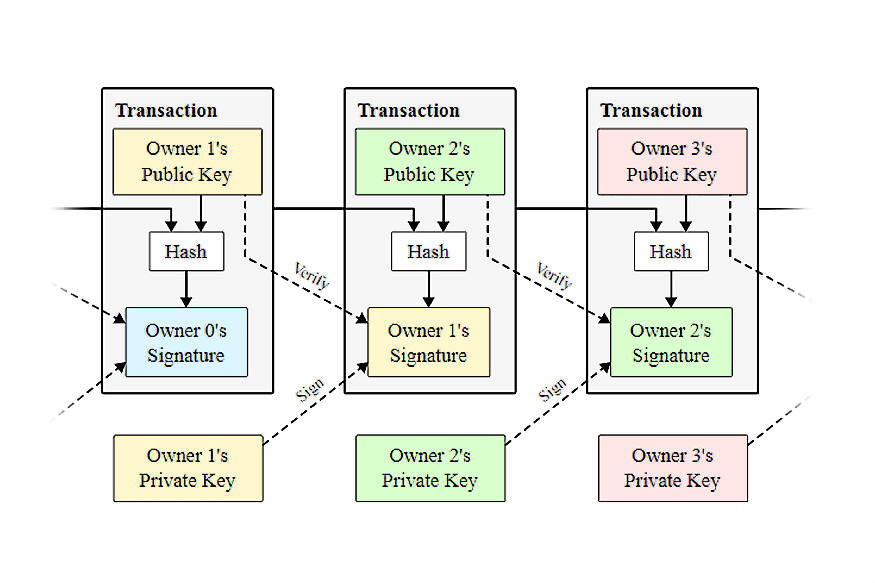
The ‘Hash' of a block can be considered as its digital signature. Each block in a blockchain contains a unique hash and can be compared to a fingerprint. If a hash of a block is changed, the block no-longer remains its original self.
The hash of the previous block is what forms the chain between these blocks. It acts as a valid proof of concept for the further blocks to act upon and is the primary security measure of a Blockchain against tampering.
Also read: Facebook's Zuckerberg Unscathed by Congressional Grilling, Stock Rises
How is it Secure?
Now that we know what is inside a block, let us have a look at how the blocks function in a chain.
As we know by now, the blocks are linked in a chain. This is done by each of the block building on the hash of the previous block. Now if in case the hash of any block is changed in a Blockchain, the consecutive blocks no longer recognise it as a valid element. This in-turn renders the entire chain useless, thus not validating any sort of tampering with any block. This is one security measure that the Blockchain provides. In case any tampering has to be made valid, the disturber will have to rework the hashes of the entire following blockchain.
In addition to this, Blockchains use a ‘Proof of Work’ concept to increase the security. A ‘Proof of Work’ can be equated to the processing time taken by a computer. This essentially slows down the creation of a new block in a Blockchain. In a Bitcoin Blockchain, for instance, it takes around 10 minutes to create a new block. So to alter an entire Blockchain, one will have to spend ten minutes on each block of a Blockchain, making the process nearly impossible.
These measures, however, do not guarantee that the value of a block cannot be changed. So there is one final security measure that Blockchains use. As discussed before, Blockchains use a ‘distributed ledger’, also known as a Peer-to-Peer network. This means that even if one manages to alter one particular copy of a Blockchain by adding a defected block, the altered block will still not be accepted into the system. This is simply because the altered block will not match with the copies that others have in a system and hence will be discarded. In order for a block to be accepted into the system, it has to pass a Consensus, meaning, it has to be validated by more than 50 percent of the network. This makes the alteration of any Blockchain almost impossible.

Also read: Does Facebook Track Your Activities Even After You Log Out? Zuckerberg Doesn't Know
Uses of Blockchain
Though the Blockchain technology was developed to create a digital time-stamp and its use was further propagated as a technology for crypto-currencies, Blockchain has immense potential in the world of technology. As of today, Blockchain is considered as the next big step in the field of Banking, Healthcare, Production, Transport and also to maintain Government records, land records and many more of such uses.
As an example, Saudi Arabia recently tied up with Ripple to use Blockchain technology in its Central Bank. Even the Indian Government has announced that the IIT Degree’s will be handed out through Blockchain technology in the year 2019. The examples are numerours, the untouched potential is huge. One thing is clear though, Blockchain can be the key to revolutionise the working in any of the industry known to humankind. Bitcoin provided us with a live and biggest example of this.
Watch: Tech and Auto Show | EP35 | Mercedes-Benz S-Class, Samsung Galaxy S9+ & More


















Comments
0 comment